Best Netherlands Authority for the Financial Markets (AFM) Regulated Brokers 2026
We’ve personally tested and ranked the top brokers regulated by the Netherlands Authority for the Financial Markets (AFM), ensuring high standards of trust and reliability.
-
1Interactive Brokers (IBKR) is a top brokerage firm offering access to 150 markets in 33 countries and a range of investment services. With 40 years in the field, this company listed on Nasdaq strictly follows the rules set by authorities such as the SEC, FCA, CIRO, and SFC. It's recognized as one of the most reliable brokers for global trading.
-
2
Trust Platform Assets Fees Accounts Research Education Mobile Support 4.9 Founded in 2006, AvaTrade is a top forex and CFD broker trusted by over 400,000 traders. Regulated in 9 regions, it handles more than 2 million trades monthly. AvaTrade offers platforms like MT4, MT5, and WebTrader, with over 1,250 instruments. Traders of all levels can explore CFDs, AvaOptions, and AvaFutures for short-term trading. AvaTrade provides excellent education and 24/5 multilingual customer support for a complete trading experience. -
3
Trust Platform Assets Fees Accounts Research Education Mobile Support 3.7 LiteForex Europe, a CFD broker certified by CySEC, was founded in 2008. It provides forex, commodities, and indices trading through the MT4 and MT5 platforms. Its ECN accounts feature extremely tight spreads, with leverage up to 1:30 per EU regulations. LiteForex also provides an extensive education center for new traders, as well as social trading features.
Compare The Top AFM-Authorized Brokers
Safety Comparison
Compare how safe the Best Netherlands Authority for the Financial Markets (AFM) Regulated Brokers 2026 are.
Mobile Trading Comparison
Compare the mobile trading features of the Best Netherlands Authority for the Financial Markets (AFM) Regulated Brokers 2026.
Comparison for Beginners
Compare how suitable the Best Netherlands Authority for the Financial Markets (AFM) Regulated Brokers 2026 are for beginners.
Comparison for Advanced Traders
Compare how suitable the Best Netherlands Authority for the Financial Markets (AFM) Regulated Brokers 2026 are for advanced or professional traders.
Accounts Comparison
Compare the trading accounts offered by Best Netherlands Authority for the Financial Markets (AFM) Regulated Brokers 2026.
Detailed Rating Comparison
Compare how we rated the Best Netherlands Authority for the Financial Markets (AFM) Regulated Brokers 2026 in key areas.
Fee and Cost Comparison
Compare the cost of trading with the Best Netherlands Authority for the Financial Markets (AFM) Regulated Brokers 2026.
Broker Popularity
See how popular the Best Netherlands Authority for the Financial Markets (AFM) Regulated Brokers [year] are in terms of number of clients.
| Broker | Popularity |
|---|---|
| Interactive Brokers |
|
| LiteForex Europe |
|
| AvaTrade |
|
Why Trade With Interactive Brokers?
Interactive Brokers is ideal for seasoned traders due to its robust charting platforms, updated data, and adaptability, especially with the IBKR Desktop application. Its exceptional pricing and advanced order features appeal to traders, and its variety of stocks remains unmatched in the market.
Pros
- IBKR is a highly regarded brokerage, regulated by prime authorities. This ensures the safety and reliability of your trading account.
- The TWS platform is designed for intermediate to advanced traders. It includes over 100 order types and a dependable real-time market data feed that rarely experiences downtime.
- Interactive Brokers has introduced ForecastTrader, a zero-commission service allowing users to trade yes/no Forecast Contracts on political, economic, and climate events. Contracts offer fixed $1 payouts, 24/6 market access, and a 3.83% APY on held positions.
Cons
- TWS's platform may be difficult for beginners to grasp because of its complexity - we were overwhelmed during our initial tests by the sheer volume of tools, features and widgets.
- Only one active session per account is allowed, which means you can't run the desktop version and mobile app at the same time. This can sometimes lead to a frustrating trading experience.
- Customer service may take time to respond, and there may be delays in fixing problems based on tests. It could be difficult to reach the customer service promptly.
Why Trade With AvaTrade?
AvaTrade provides traders with essential tools: an intuitive WebTrader, strong AvaProtect risk management, a quick 5-minute sign-up, and reliable support for fast-paced markets.
Pros
- AvaTrade introduced AvaFutures for low-margin global market access and expanded in 2025 by adding CME’s Micro Grain Futures. Later that year, they integrated with TradingView.
- The WebTrader performed well in our tests, featuring an easy-to-use interface for beginners and strong charting tools, including 6 chart layouts and over 60 technical indicators.
- AvaTrade's support team did well in tests, responding within 3 minutes and providing local support in major regions like the UK, Europe, and the Middle East.
Cons
- Signing up is easy, but AvaTrade doesn't offer an ECN account like Pepperstone or IC Markets, which provides raw spreads and fast execution that many traders want.
- The AvaSocial app is satisfactory but could be better. Its design, usability, and navigation between strategy providers and account management need improvement to compete with top platforms like eToro.
- While the deposit process is smooth, AvaTrade doesn't support crypto payments, unlike TopFX, which caters to crypto-focused traders.
Why Trade With LiteForex Europe?
LiteForex is a suitable choice for active traders due to its variable spreads starting from 0.0 pips, daily analysis and comprehensive training guides. Traders can also replicate the strategies of skilled traders through its forex copy system.
Pros
- LiteForex provides each trader with a personal manager and offers 24/5 customer support in multiple languages.
- Quickest ECN model with minimal spreads starting at 0.0 pips for trading.
- LiteForex provides its own mobile apps that are great for traders who need to examine the markets while mobile.
Cons
- Fees are relatively expensive. The Classic account has spreads starting at 2.0 pips, while the ECN account charges $10 forex commissions.
- The options for trading markets are more limited, as share CFDs are not available.
- The funding options are fewer than other brands.
Filters
How BrokerListings.com Chose The Top AFM Brokers
To find the top brokers licensed by the AFM in the Netherlands, we followed a strict verification and evaluation process:
- First, we confirmed each broker’s regulatory status directly through the official register of the Autoriteit Financiële Markten (AFM), ensuring they are legally authorized to operate in the Dutch market.
- We then combined detailed platform testing with over 200 performance metrics to rank brokers based on reliability, costs, trading tools, and suitability for active traders.
What Is The AFM?
The Authority for the Financial Markets (AFM) is tasked with regulating and supervising financial markets in the Netherlands.
Set up in 2002, the organization “supervises the conduct of the entire financial market sector: savings, investment, insurance, loans, pensions, capital markets, asset management, accountancy and financial reporting.”
To operate in the Dutch marketplace, financial brokerages need to be authorized by the AFM. We feel consumers enjoy robust protections when using such companies: under BrokerListing.com’s broker regulator classification system, the AFM holds a Category A rating.
As well as issuing licenses, the regulator will monitor the actions of the country’s brokers and initiate enforcement action when required.
What Powers Does AFM Have?
According to its website, the AFM “conducts its supervision by means of inspections, enforcement and transfer of standards, and in so doing expressly monitors signals originating from the market and findings from its own control organization.”
If it finds evidence of regulatory breaches, the AFM has a range of formal enforcement tools it may draw upon. It can, for instance:
- Issue instructions that mandate companies to take certain actions.
- Put institutions under undisclosed custody.
- Cancel or refuse registrations.
- Publish public warnings.
- Appoint a conservator to monitor the activities of organizations and individuals.
- Impose one-off fines and orders for periodic financial penalties.
- Withdraw licenses.
- File reports with the Netherlands’ Public Prosecution Service.
The AFM can also initiate informal proceedings when it deems an offence has been committed. These take the form of a supervisory letter or conversation for minor infractions, or warning letters or conversations for more serious breaches.
In one high profile case, the regulator slapped a €530,000 administrative fine on BinckBank in 2023, which traded under the name Saxo Bank. The AFM deemed that “from December 2019 to December 2021, BinckBank did not have procedures and measures in place to safeguard that clients only invested in financial products appropriate for the target market to which they belonged.”
What Rules Must An AFM Broker Follow?
As a member of the European Union, the Netherlands tailors its financial market regulations in accordance with those devised by the European Securities and Markets Association (ESMA).
ESMA’s mission “is to enhance investor protection, promote orderly financial markets and safeguard financial stability” across European Economic Area (EEA) countries. This bloc comprises all 27 European Union member states alongside Norway, Iceland and Liechtenstein.
AFM’s licensing, supervisory and enforcement actions are aligned with principles in the Markets in Financial Instruments Directive II (MiFID II), launched in 2018 by ESMA.
MiFID II states that financial services providers must act “honestly, fairly and professionally,” and with “the best interests of its clients” at the heart of everything they do.
Some of the directive’s key requirements include:
- Strive for the best possible results: brokerages must seek the most favourable trading result for their client based on “price, costs, speed, likelihood of execution and settlement, size, nature or any other consideration.”
- Ascertain product suitability: companies must determine their clients’ financial knowledge, experience, financial situation, and investment objectives to ensure the products or services discussed “are suitable for him and, in particular, are in accordance with his risk tolerance and ability to bear losses.”
- Provide clear and true information: information for customers and potential clients “shall be fair, clear and not misleading,” while “marketing communications shall be clearly identifiable as such.”
- Safeguard client assets: brokers must “make adequate arrangements so as to safeguard the ownership rights of clients… and to prevent the use of a client’s financial instruments,” except with the customer’s express permission.
- Keep extensive records: companies “shall arrange for records to be kept of all services, activities and transactions” they undertake for supervisory and potential enforcement purposes.
How Can I Check If A Brokerage Is AFM Regulated?
Traders and investors can check a company’s regulatory status using the ‘Registers’ section on the AFM’s website:
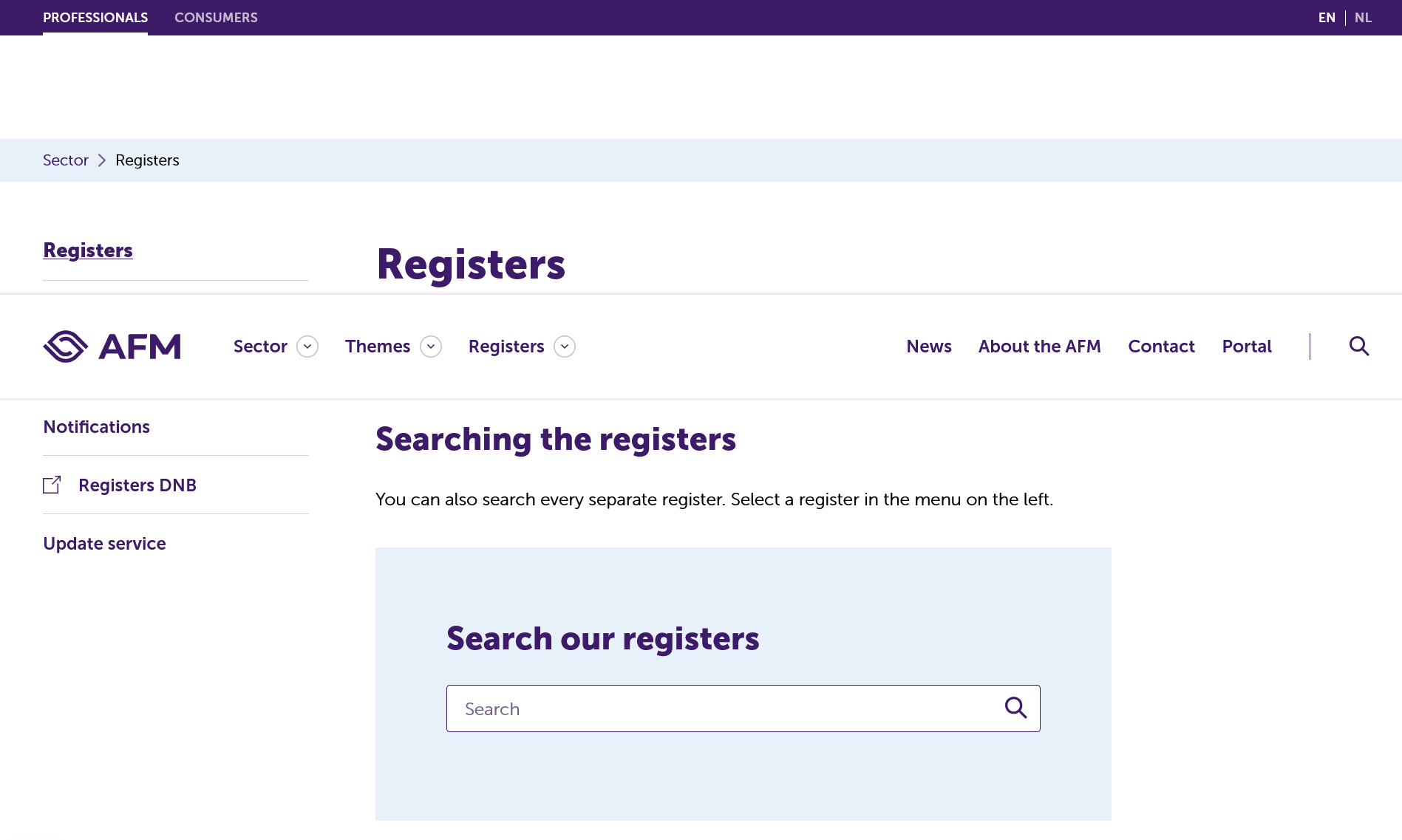
Individuals can search for licensed brokers. Source: AFM
I wanted to check the regulatory status of LiteForex Europe, a brokerage I believed was AFM registered. I typed the name of the company in the ‘Search our registers’ field and was greeted with the following result:
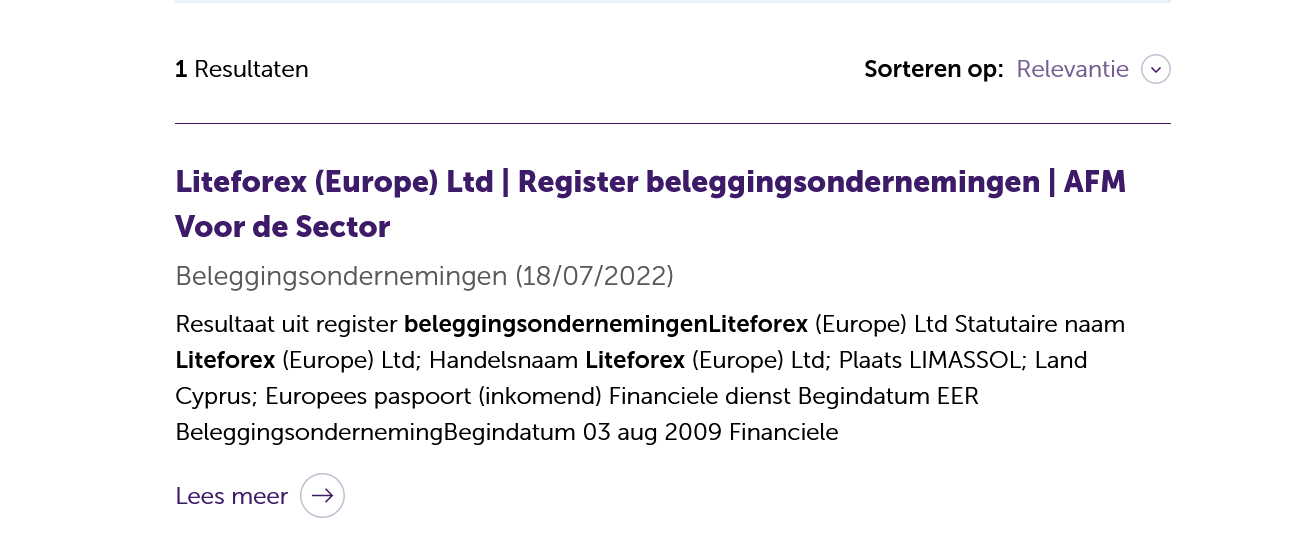
Locating LiteForex Europe on the Registers database. Source: AFM
Clicking on the name of the company yielded further information:
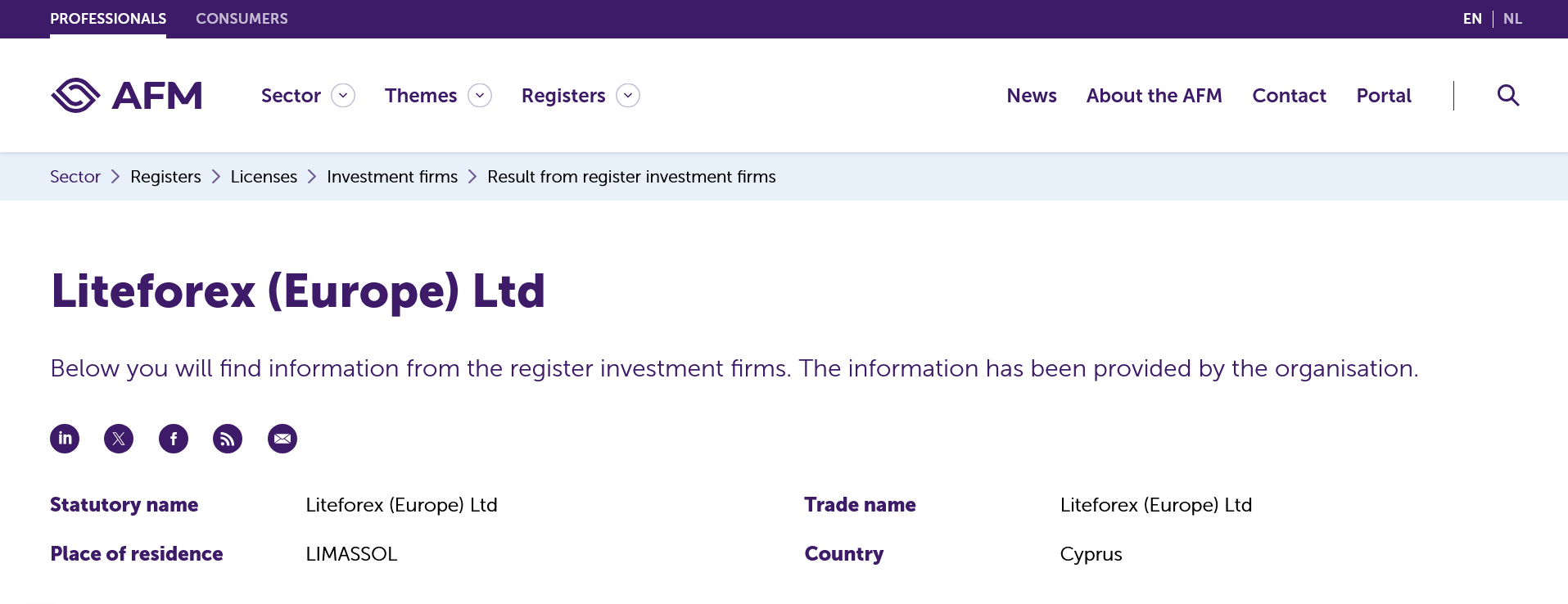
LiteForex Europe’s full profile. Source: AFM
As a non-Dutch speaker, I toggled the language option at the top-right of the screen, selecting ‘EN’ to read the company’s registration details in English. Here I found information such as where the broker is registered, and when it notified the AFM of its intention to provide services in the Netherlands.
My search also showed that while LiteForex Europe isn’t directly regulated by the AFM, it is permitted to do business in the Netherlands under MiFID II passporting rules. In this case, the broker is licensed by the Cyprus Securities and Exchange Commission (CySEC), another Category A regulator under BrokerListings.com’s rating system.
Passporting allows financial services companies to trade in EEA countries without having to register with multiple regulators. As long as they’re authorized and supervised in one EEA member state, and inform the regulator in another member country of their intention to trade there, they’re good to go.
Pro tip: The AFM also maintains a public warnings list on its website to help traders and investors avoid bad actors. This can include companies and individuals that have been found to be operating without a license, or firms that have not issued a prospectus for the products they offer.
Unfortunately, the warnings list and the related pages are only published in Dutch. However, individuals can get around this by using a standard browser translation tool (such as Google Translate). Here’s how the search facility looked when I translated the page into English:
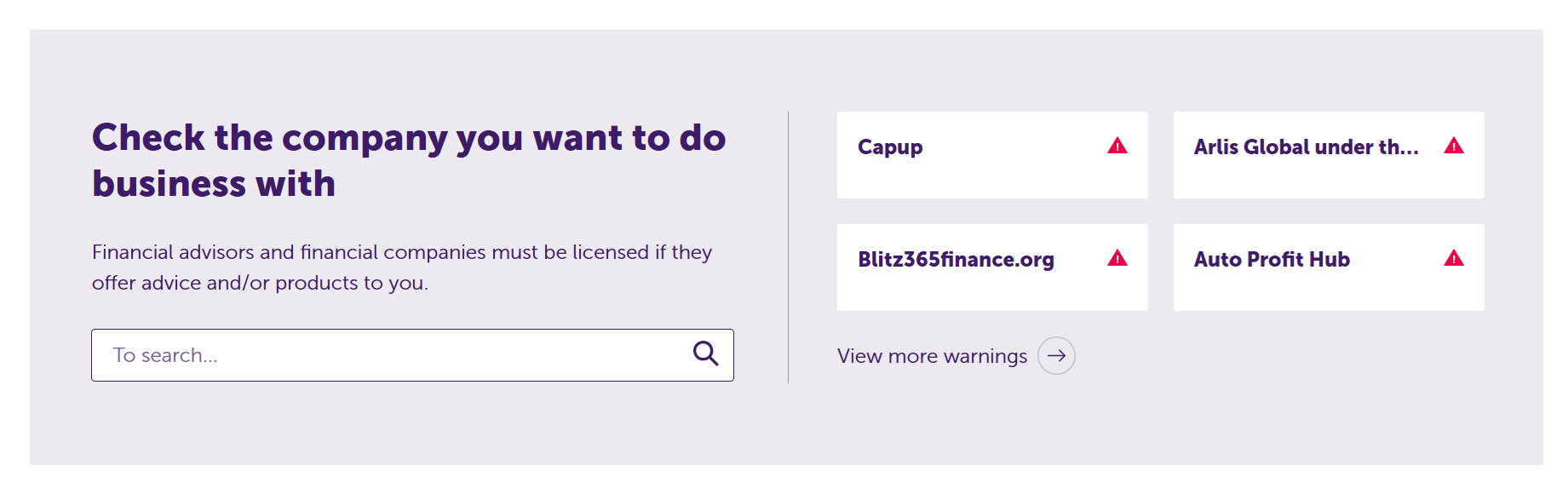
Search options for AFM warnings. Source: AFM
I can click on the boxes with the red upward arrows to view the AFM’s most recent warnings. I’m also able to punch in a broker’s name for a targeted search, or click on the ‘View more warnings’ option for an alphabetical list of historical warnings.
Bottom Line
The Netherlands’ status as an EEA member state means traders and investors receive exceptional protection when dealing in the country’s financial markets.
Using AFM-approved brokers can substantially reduce the chances of them experiencing fraud and improve their overall trading experience.
Article Sources
Authority for the Financial Markets (AFM)
What measures can the AFM impose? – AFM
AFM fines BinckBank for infringement of product governance rules – AFM
European Securities and Markets Association (ESMA)
Markets in Financial Instruments Directive II (MiFID II)
What is ‘passporting’ and why does it matter? – UK Finance


